3D Printing Transformations in Building Exteriors
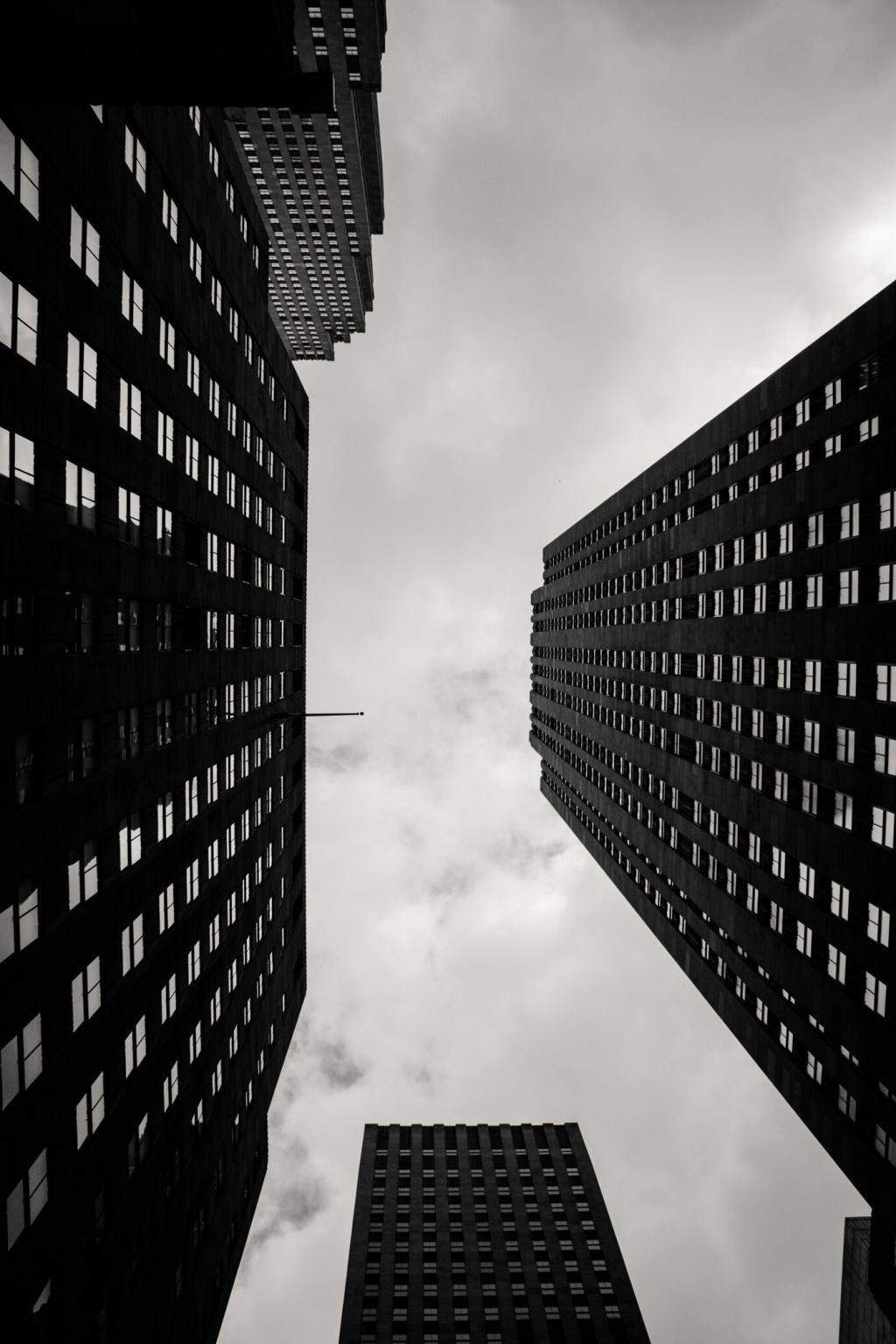
The field of construction has witnessed groundbreaking innovations in recent years, and among the most revolutionary is 3D printing technology. This digital fabrication method is redefining how building exteriors are designed, constructed, and maintained. With the ability to produce complex shapes, intricate details, and bespoke facade solutions, 3D printing introduces new possibilities in sustainability, design freedom, and speed. This page explores how 3D printing is transforming the appearance, function, and performance of building exteriors across modern architecture.
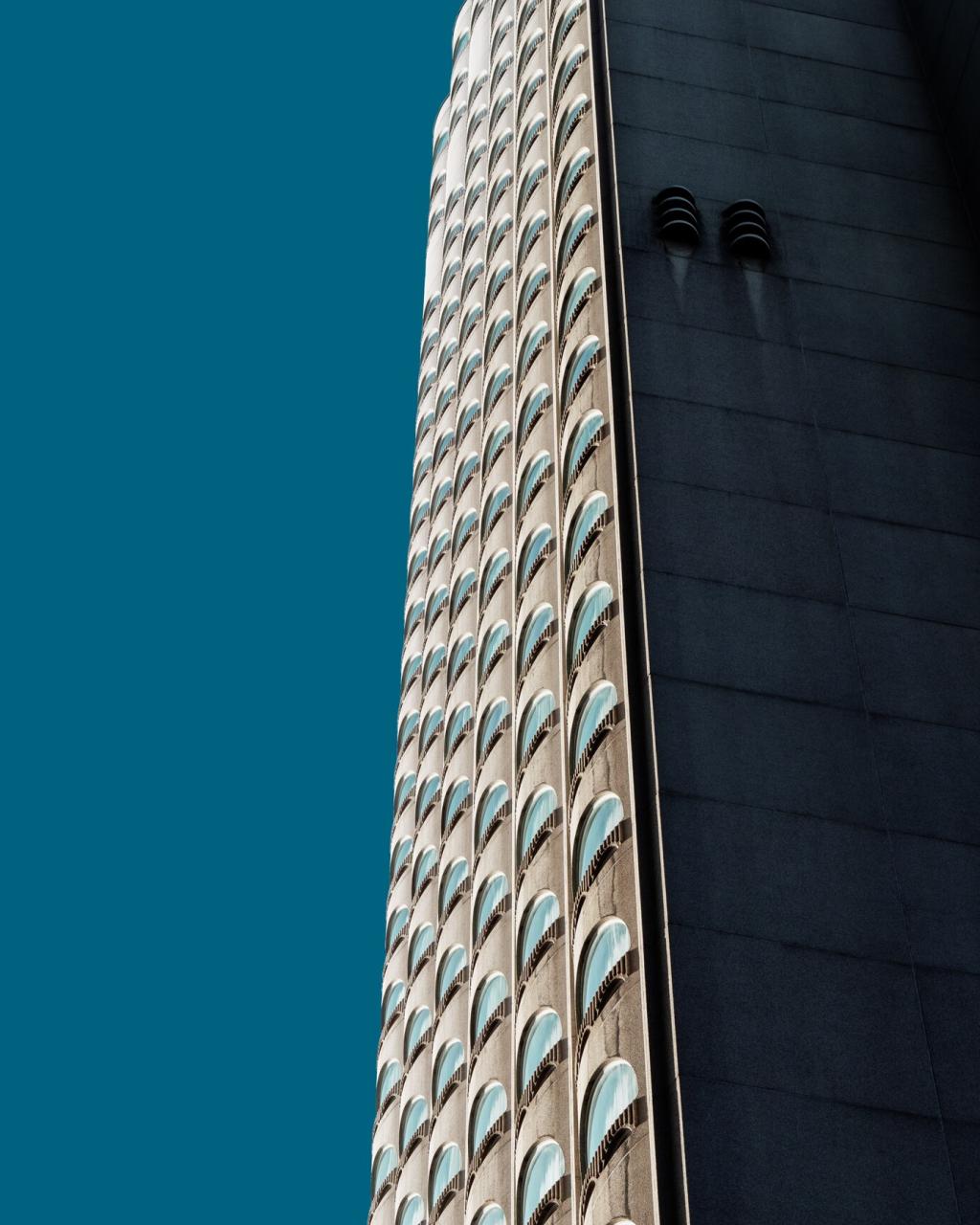

Redefining Architectural Expression with 3D Printing
Customization Beyond Traditional Methods
3D printing makes it possible to individualize each component of a building’s exterior. While conventional methods required mass production of identical pieces, digital fabrication enables adjustments to dimensions, aesthetics, and functionalities with ease. Automated production allows for the replication of intricate motifs, parametric features, or cultural references on every facade or surface panel. This level of customization gives clients, developers, and communities the chance to own buildings that truly reflect their vision and context, moving beyond standard templates and generic appearances.
Innovative Material Applications
Integration of unconventional materials into building exteriors has reached new heights thanks to 3D printing. Modern printers use not just plastics, but also concrete, composites, and even recycled materials to create durable and visually appealing façades. Such versatility allows architects to experiment with textures, transparency, and color, offering designers a palette that was previously impossible. The technology also enables structural integration within panels—like insulation or complex lattices—making exteriors perform better environmentally.
Advanced Facade Functions
With 3D printing, exteriors are evolving from simple enclosures to multifunctional skins. Panels can be fabricated with integrated ventilation channels, solar shading devices, or rainwater harvesting systems, embedded directly during the printing process. This approach supports building performance by improving thermal comfort, reducing environmental impact, and delivering smarter, more responsive envelope systems. The ease with which such features can be incorporated is transforming traditional facades into dynamic, efficient, and interactive systems.
Accelerating Construction Timelines
Digital-to-Physical Workflow Efficiency
The translation of digital models directly into physical facade components eliminates many intermediate steps associated with traditional construction. Once a design is finalized, files are sent directly to 3D printers, which produce the required components with precision and minimal waste. This seamless workflow increases production accuracy, supports prefabrication off-site, and minimizes the risks associated with human error or material defects, leading to faster, more reliable exterior assembly.
Streamlining On-Site Installation
Prefabricated 3D-printed panels or modules are often lightweight and designed with integrated connections, simplifying transportation and on-site assembly. Instead of relying on extensive scaffolding or manual fitting, components can be directly attached to the building’s structure, dramatically reducing installation time. This efficiency is particularly valuable in projects with tight deadlines or difficult site conditions, allowing entire façade systems to be installed in record time with less disruption to surrounding areas.
Enabling Design Revisions During Construction
Because 3D-printed elements can be produced rapidly, design adjustments can be accommodated even late in the construction process. If unforeseen challenges or client preferences arise, digital models can be updated and new facade components printed without significant delays. This flexibility fosters a more adaptive and responsive approach to building, ensuring that the realized exterior aligns with stakeholders’ evolving expectations while keeping the project on track.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Traditional construction techniques often involve cutting, shaping, and combining materials, leading to significant offcuts and waste. In contrast, 3D printing is an additive manufacturing process, meaning materials are deposited only where needed in exact quantities. This not only leads to substantial reductions in material waste but also translates into cost savings and improved resource management. Over time, wide-scale adoption of this technology could dramatically lessen landfill contributions from construction debris.